Welcome to the Hardcore Husky Forums. Folks who are well-known in Cyberland and not that dumb.
Sark is in rehab
Comments
-
Pics?TierbsHsotBoobs said:Beat COOG. Nothing Else Matters.
-
Must have?gmo said:good poont, CuntWaffle. Seven Patrons must have been wasted when he started the Go Huskies chant at Don James' funeral.
-
I can't wait for the UW stories to break out. You know players like Hartvingson have been waiting for this.
-
Dick Baird's Twitter name must be Spencer Checketts
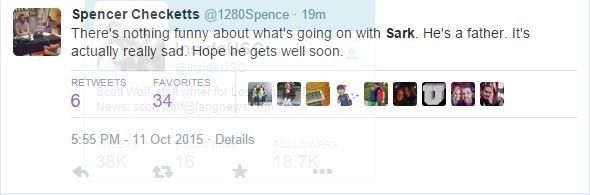
-
I love the people saying Sark is "sick".
-
D
so is Jared Fogle. What is their point?CuntWaffle said:I love the people saying Sark is "sick".
-
AlcoholismCuntWaffle said:I love the people saying Sark is "sick".
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Alcoholism, also known as alcohol use disorder (AUD) and alcohol dependence syndrome, is a broad term for any drinking of alcohol that results in problems.[1] It was previously divided into two types: alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence.[2][3] In a medical context alcoholism is said to exist when two or more of the following is present: a person drinks large amounts over a long time period, has difficulty cutting down, acquiring and drinking alcohol takes up a great deal of time, alcohol is strongly desired, usage results in not fulfilling responsibilities, usage results in social problems, usage results in health problems, usage results in risky situations, withdrawal occurs when stopping, and alcohol tolerance has occurred with use.[3] Alcohol use can affect all parts of the body but particularly affects the brain, heart, liver, pancreas, and immune system. This can result in mental illness, Wernicke Korsakoff syndrome, an irregular heart beat, liver failure, and an increase the risk of cancer, among other disease.[4][5] Drinking during pregnancy can cause damage to the baby resulting in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.[6] Generally women are more sensitive to alcohol's harmful physical and mental effects than men.[7]
Both environmental factors and genetics are involved in causing alcoholism with about half the risk attributed to each. A person with a parent or sibling with alcoholism are three to four times more likely to be alcoholic themselves.[4] Environmental factors include social, cultural, and behavioral influences.[8] High stress levels, anxiety, as well as inexpensive easily accessible alcohol increases risk.[4][9] People may continue to drink partly to prevent or improve symptoms of withdrawal. A low level of withdrawal may last for months following stopping.[4] Medically alcoholism is considered both a physical and mental illness.[10][11] Both questionnaires and certain blood tests may detect people with possible alcoholism. Further information is then collected to confirm the diagnosis.[4]
Prevention of alcoholism is possible by regulating and limiting the sale of alcohol, taxing alcohol to increase its cost, and providing inexpensive treatment.[12] Treatment may take several steps. Because of the medical problems that can occur during withdrawal, alcohol detoxification should be carefully controlled. One common method involves the use of benzodiazepine medications, such as diazepam. This can be either given while admitted to a health care institution or occasionally while a person remains in the community with close supervision.[13] Other addictions or mental illness may complicate treatment.[14] After detoxification support such as group therapy or support groups are used to help keep a person from returning to drinking.[15][16] One commonly used form of support is the group Alcoholics Anonymous.[17] The medications acamprosate, disulfiram, or naltrexone may also be used to help prevent further drinking.[18]
The World Health Organization estimates that as of 2010 there were 208 million people with alcoholism worldwide (4.1% of the population over 15 years of age).[7][19] In the United States about 17 million (7%) of adults and 0.7 million (2.8%) of those age 12 to 17 years of age are affected.[20] It is more common among males and young adults, becoming less common in middle and old age.[4] It is the least common in Africa at 1.1% and has the highest rates in Eastern Europe at 11%.[4] Alcoholism directly resulted in 139,000 deaths in 2013 up from 112,000 deaths in 1990.[21] A total of 3.3 million deaths (5.9% of all deaths) are believed to be due to alcohol.[20] It often reduces a person's life expectancy by around ten years.[22] In the United States it resulted in economic costs of $224 billion USD in 2006.[20] Many terms, some insulting and others informal, have been used to refer to people affected by alcoholism including: tippler, drunkard, dipsomaniac, and souse.[23] In 1979, the World Health Organization discouraged the use of "alcoholism" due to its inexact meaning, preferring "alcohol dependence syndrome".[24]
Contents
1 Signs and symptoms
1.1 Early signs
1.2 Long-term misuse
1.3 Alcohol withdrawal
2 Causes
2.1 Alcohol availability
2.2 Gender difference
2.3 Genetic variation
3 Diagnosis
3.1 Definition
3.2 Social barriers
3.3 Screening
3.4 Genetic predisposition testing
3.5 Urine and blood tests
4 Prevention
5 Management
5.1 Detoxification
5.2 Psychological
5.3 Medications
5.4 Dual addictions and dependences
6 Epidemiology
7 Prognosis
8 History
9 Society and culture
10 Research
11 See also
12 References
13 Further reading
14 External links
Signs and symptoms
File:What Alcohol Does to Your Body.webmPlay media
Effects of alcohol on the body
Early signs
The risk of alcohol dependence begins at low levels of drinking and increases directly with both the volume of alcohol consumed and a pattern of drinking larger amounts on an occasion. Young adults are particularly at risk.
Long-term misuse
Some of the possible long-term effects of ethanol an individual may develop. Additionally, in pregnant women, alcohol can cause fetal alcohol syndrome.
Alcoholism is characterised by an increased tolerance to and physical dependence on alcohol, affecting an individual's ability to control consumption. These characteristics play a role decreasing an alcoholic's ability to stop drinking.[25] Alcoholism can have adverse effects on mental health, causing psychiatric disorders and increasing the risk of suicide. A depressed mood is a common symptom.[26][27]
Physical
Long-term alcohol abuse can cause a number of physical symptoms, including cirrhosis of the liver, pancreatitis, epilepsy, polyneuropathy, alcoholic dementia, heart disease, nutritional deficiencies, peptic ulcers[28] and sexual dysfunction, and can eventually be fatal. Other physical effects include an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, malabsorption, alcoholic liver disease, and cancer. Damage to the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system can occur from sustained alcohol consumption.[29][30] A wide range of immunologic defects can result and there may be a generalized skeletal fragility, in addition to a recognized tendency to accidental injury, resulting a propensity to bone fractures.[31]
Women develop long-term complications of alcohol dependence more rapidly than do men. Additionally, women have a higher mortality rate from alcoholism than men.[32] Examples of long-term complications include brain, heart, and liver damage[33] and an increased risk of breast cancer. Additionally, heavy drinking over time has been found to have a negative effect on reproductive functioning in women. This results in reproductive dysfunction such as anovulation, decreased ovarian mass, problems or irregularity of the menstrual cycle, and early menopause.[32] Alcoholic ketoacidosis can occur in individuals who chronically abuse alcohol and have a recent history of binge drinking.[34][35]
The amount of alcohol that can be biologically processed and its effects differ between sexes. Equal dosages of alcohol consumed by men and women generally result in women having higher blood alcohol concentrations (BACs), since women generally have a higher percentage of body fat and therefore a lower volume of distribution for alcohol than men, and because the stomachs of men tend to metabolize alcohol more quickly.[36]
Psychiatric
Long-term misuse of alcohol can cause a wide range of mental health problems. Severe cognitive problems are common; approximately 10 percent of all dementia cases are related to alcohol consumption, making it the second leading cause of dementia.[37] Excessive alcohol use causes damage to brain function, and psychological health can be increasingly affected over time.[38]
Social skills are significantly impaired in people suffering from alcoholism due to the neurotoxic effects of alcohol on the brain, especially the prefrontal cortex area of the brain. The social skills that are impaired by alcohol abuse include impairments in perceiving facial emotions, prosody perception problems and theory of mind deficits; the ability to understand humour is also impaired in alcohol abusers.[39]
Psychiatric disorders are common in alcoholics, with as many as 25 percent suffering severe psychiatric disturbances. The most prevalent psychiatric symptoms are anxiety and depression disorders. Psychiatric symptoms usually initially worsen during alcohol withdrawal, but typically improve or disappear with continued abstinence.[40] Psychosis, confusion, and organic brain syndrome may be caused by alcohol misuse, which can lead to a misdiagnosis such as schizophrenia.[41] Panic disorder can develop or worsen as a direct result of long-term alcohol misuse.[42][43]
The co-occurrence of major depressive disorder and alcoholism is well documented.[44][45][46] Among those with comorbid occurrences, a distinction is commonly made between depressive episodes that remit with alcohol abstinence ("substance-induced"), and depressive episodes that are primary and do not remit with abstinence ("independent" episodes).[47][48][49] Additional use of other drugs may increase the risk of depression.[50]
Psychiatric disorders differ depending on gender. Women who have alcohol-use disorders often have a co-occurring psychiatric diagnosis such as major depression, anxiety, panic disorder, bulimia, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or borderline personality disorder. Men with alcohol-use disorders more often have a co-occurring diagnosis of narcissistic or antisocial personality disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, impulse disorders or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.[51] Women with alcoholism are more likely to have a history of physical or sexual assault, abuse and domestic violence than those in the general population,[51] which can lead to higher instances of psychiatric disorders and greater dependence on alcohol.
Social effects
See also: Drug-related crime
The social problems arising from alcoholism are serious, caused by the pathological changes in the brain and the intoxicating effects of alcohol.[37][52] Alcohol abuse is associated with an increased risk of committing criminal offences, including child abuse, domestic violence, rape, burglary and assault.[53] Alcoholism is associated with loss of employment,[54] which can lead to financial problems. Drinking at inappropriate times, and behavior caused by reduced judgment, can lead to legal consequences, such as criminal charges for drunk driving[55] or public disorder, or civil penalties for tortious behavior, and may lead to a criminal sentence.
An alcoholic's behavior and mental impairment, while drunk, can profoundly affect those surrounding them and lead to isolation from family and friends. This isolation can lead to marital conflict and divorce, or contribute to domestic violence. Alcoholism can also lead to child neglect, with subsequent lasting damage to the emotional development of the alcoholic's children.[56] For this reason, children of alcoholic parents can develop a number of emotional problems. For example, they can become afraid of their parents, because of their unstable mood behaviors. In addition, they can develop considerable amount of shame over their inadequacy to liberate their parents from alcoholism. As a result of this failure, they develop wretched self-images, which can lead to depression.[57]
Alcohol withdrawal
Main article: Alcohol withdrawal syndrome
See also: Kindling (sedative-hypnotic withdrawal)
As with similar substances with a sedative-hypnotic mechanism, such as barbiturates and benzodiazepines, withdrawal from alcohol dependence can be fatal if it is not properly managed.[52][58] Alcohol's primary effect is the increase in stimulation of the GABAA receptor, promoting central nervous system depression. With repeated heavy consumption of alcohol, these receptors are desensitized and reduced in number, resulting in tolerance and physical dependence. When alcohol consumption is stopped too abruptly, the person's nervous system suffers from uncontrolled synapse firing. This can result in symptoms that include anxiety, life-threatening seizures, delirium tremens, hallucinations, shakes and possible heart failure.[59][60] Other neurotransmitter systems are also involved, especially dopamine, NMDA and glutamate.[25][61]
Severe acute withdrawal symptoms such as delirium tremens and seizures rarely occur after 1 week post cessation of alcohol. The acute withdrawal phase can be defined as lasting between one and three weeks. In the period of 3 – 6 weeks following cessation increased anxiety, depression as well as sleep disturbance is common;[62] fatigue and tension can persist for up to 5 weeks as part of the post-acute withdrawal syndrome; about a quarter of alcoholics experience anxiety and depression for up to 2 years. These post-acute withdrawal symptoms have also been demonstrated in animal models of alcohol dependence and withdrawal.[63] A kindling effect also occurs in alcoholics whereby each subsequent withdrawal syndrome is more severe than the previous withdrawal episode; this is due to neuroadaptations which occur as a result of periods of abstinence followed by re-exposure to alcohol. Individuals who have had multiple withdrawal episodes are more likely to develop seizures and experience more severe anxiety during withdrawal from alcohol than alcohol dependent individuals without a history of past alcohol withdrawal episodes. The kindling effect leads to persistent functional changes in brain neural circuits as well as to gene expression.[64] Kindling also results in the intensification of psychological symptoms of alcohol withdrawal.[62] -
I'm a terrible person for not wanting to "support" a grown man who has a job that 99.99999% of the world could only dream of having.GrundleStiltzkin said:
-
-
The inexorable link between boozing and womanizing is clear and if you miserable twits can't see that, Grinolds and his armoir of Cuervo can't help you





